
by Rishi | Nov 5, 2019 | Jntufastupdates

Jawaharlal Nehru Technological University, Kakinada (JNTUK) has proclaimed the B.Tech II year II Semester R16, R13, R10 Supplementary Examination Time Tables November 2019 on it’s official web site. The Candidates WHO ar trying to find the 2-2 sem agenda, All those candidates ar requested to transfer the 2-2 sem R16, R13, R10 Time Tables 2019 from below. After that, the scholars ar suggested to start out making ready for the semester examinations.
JNTUK 2-2 Time Tables 2019 For R16, R13, R10
You can conjointly get the regular and supplementary examination Jumbling Centres from the official web site or here. As per the schedule, the examination are going to be control from weekday, fifteenth November 2019 and Conclude on weekday, twenty seventh November, 2019.
Details of JNTUK 2-2 offer Exams November 2019:
Name of the University Jawaharlal solon Technological University, Kakinada
Name Of the Exam B.Tech 2-2 Sem (R16, R13, R10) offer Exams, Nov 2019
Exams Starts From 15-11-2019 (Friday)
Conclude on 27-11-2019 (Wednesday)
Timings 2.00 PM TO 5.00 PM
Jawaharlal Nehru Technological University, Kakinada (JNTU Kakinada) may be a public university, placed at Pithapuram Road in Kakinada. the faculty offers numerous programs and conducts the semester examinations per annum.
The following Examination time tables ar discharged by JNTU-KKD
II B.TECH – II SEMESTER (R16 REGULATIONS) SUPPLEMENTARY EXAMINATIONS, November – 2019
II B.TECH – II SEMESTER (R13 REGULATIONS) SUPPLEMENTARY EXAMINATIONS, November – 2019
II B.TECH – II SEMESTER (R10 REGULATIONS) SUPPLEMENTARY EXAMINATIONS, November – 2019
All the higher than Examinations are going to be conducted in jumbling system.
Download the time tables from links given below:
JNTUK 2-2 Sem R16 Time Table November month 2019
JNTUK 2-2 Sem R13 Time Table Nov 2019
JNTUK 2-2 Sem R10 Time Table Nov 2019
NOTE:
i. ANY OMISSIONS OR CLASHES during this agenda could PLEASE learn TO THE CONTROLLER OF EXAMINATIONS, like a shot.
ii. notwithstanding GOVERNMENT DECLARES vacation ON ANY OF THE higher than DATES, THE EXAMINATIONS SHALL BE CONDUCTED as was common.
iii. THE PRINCIPALS ar requested to tell THE UNIVERSITY the other SUBSTITUTE SUBJECTS THAT don’t seem to be INCLUED within the higher than LIST like a shot.
How To transfer JNTUK 2-2 offer Time Tables 2019
The candidates WHO ar finding out JNTUK 2-2 offer agenda 2019 you may have to be compelled to visit the Official web site or click on the higher than links.
Find the “Download button” Click thereon.
After this method Your communicating agenda pdf are going to be downloaded.
Save and print for communicating.
All the most effective.
by Rishi | Aug 15, 2019 | Jntufastupdates
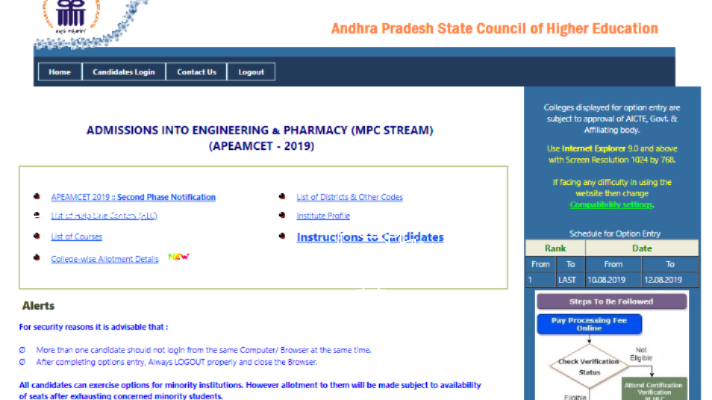
AP EAMCET Second Seat Allotment Results 2019:
Andhra Pradesh EAMCET 2nd phase allotment results from college wise released at apeamcet.nic.in.
Candidates can download AP Eamcet allotment order 2019 from the official website which is mentioned in the below links.
AP EAMCET 2nd Counselling Seat Allotment Results in 2019 – College Wise Allotment order Download @ apeamcet.nic.in
AP EAMCET Seat Allotment Order:
At last AP EAMCET board reveal the date of Ap Eamcet seat allotment results at apeamcet.nic.in. From June onwards Ap Eamcet board wants to conduct first phase counseling.
They will verify the certificates and you can choose options after completion of verification, AP eamcet 2019 allotment order download at apeamcet.nic.in.
Andhra Pradesh EAMCET 2019 2nd/second phase counseling seat’s allotment going to announce on 14-08-2019. The students who are participated in the 2nd phase counseling download your allotment order at Eamcet official web portal.
In the 2nd phase, eamcet counseling approximately 1 lakh+ students are registered their web options. AP EAMCET board to be announced seat allotment Details.
AP EAMCET Counselling Dates 2019
| S. No. | Events | Important Dates |
| 1. | Document/ Certificate Verification, Processing Fee Pay online | August 2019 |
| 2. | Web Option Entry (For College Selection) | 10th to 12th August |
| 3. | Change in Options | 10th to 12th August |
| 4. | EAMCET Seat Allotment College wise | 14th August 5 |
| 5. | Engineering Colleges/ Classes Starts from | ________________ |
Download AP EAMCET Seat Allotment Result & Allotment Order
The 2nd counseling result allotment of seats is made available on 14-08-2019 and placed on the website https://apeamcet.nic.in.
For downloading the candidate’s provisional allotment order, enter the AP EAMCET Hall Ticket Number, Password and Date of Birth in Candidate login in https://apeamcet.nic.in.
Allotments now made are subject to the grant of affiliation from the University. AP EAMCET 2nd allotment order issues Date & Time:
AP EAMCET 2nd Seat Allotment Results 2019 released. Download Allotment Order by Signing-In through ‘Candidates Login’ From Below
AP EAMCET 2019 second Seat allotment order Download – Available Now
AP EAMCET 2019 2nd College Wise Seat Allotment Details – Available Now
How to Check AP EAMCET Seat allotment Results 2019
1. Visit the ap eamcet official website: apeamcet.nic.in
2. Click on the Candidates Login Button at menu bar
3. Enter your Registration Number, date of birth, hall ticket number & password.
4. when login into your account click on the download allotment order button.
5. Take a print out & submit college
6. Done
by Rishi | Jul 30, 2019 | Jntuk lecture notes
SIGNALS & SYSTEMS
OBJECTIVES:
The main objectives of this course square measure given below:
• To introduce the word of signals and systems.
• To introduce Fourier tools through the analogy between vectors and signals.
• To introduce the idea of sampling and reconstruction of signals.
• to research the linear systems in time and frequency domains.
• to check z-transform as mathematical tool to research discrete-time signals and systems.
UNIT- I: INTRODUCTION:
Definition of Signals and Systems, Classification of Signals, Classification of Systems, Operations on signals: time-shifting, time-scaling, amplitude-shifting, amplitude-scaling. issues on classification and characteristics of Signals and Systems. advanced exponential and curving signals, Singularity operates and connected functions: impulse function, step operate signum operate and ramp operate. Analogy between vectors and signals, orthogonal signal house, Signal approximation exploitation orthogonal functions, Mean sq. error, closed or complete set of orthogonal functions, Orthogonality in advanced functions.
UNIT –II: series AND FOURIER TRANSFORM:
series illustration of continuous time periodic signals, properties of series, Dirichlet’s conditions, pure mathematics series and Exponential series, advanced Fourier spectrum. explanation Fourier remodel from series, Fourier remodel of impulsive signal, Fourier remodel of normal signals, Fourier remodel of periodic signals, properties of Fourier transforms, Fourier transforms involving impulse operate and Signum operate. Introduction to David Hilbert remodel.
UNIT –III: SAMPLING THEOREM –
Graphical and analytical proof for Band restricted Signals, impulse sampling, Natural and Flat prime Sampling, Reconstruction of signal from its samples, impact of beneath sampling – Aliasing, Introduction to Band Pass sampling.
UNIT-IV: ANALYSIS OF LINEAR SYSTEMS:
Linear system, impulse response, Response of a linear system, Linear time invariant (LTI) system, Linear time variant (LTV) system, idea of convolution in time domain and frequency domain, Graphical illustration of convolution, Transfer operate of a LTI system. Filter characteristics of linear systems. Distortion less transmission through a system, Signal information measure, system information measure, Ideal LPF, HPF and BPF characteristics, relation and Poly-Wiener criterion for physical realization, relationship between information measure and rise time.
Cross-correlation and auto-correlation of functions, properties of correlation operate, Energy density spectrum, Parseval’s theorem, Power density spectrum, Relation between motor vehicle correlation operate and energy/power spectral density operate. Relation between convolution and correlation, Detection of periodic signals within the presence of noise by correlation, Extraction of signal from noise by filtering.
UNIT –V:
Pierre Simon de Laplace|Pierre Simon de Laplace|mathematician|astronomer|uranologist|stargazer} TRANSFORMS : Review of Laplace transforms, Partial fraction enlargement, Inverse Marquis de Laplace remodel, idea of region of convergence (ROC) for Marquis de Laplace transforms, constraints on mythical monster for varied categories of signals, Properties of L.T’s, Relation
between L.T’s, and F.T. of a proof. Marquis de Laplace remodel of bound signals exploitation wave shape synthesis.
UNIT –VI:
Z–TRANSFORMS : basic distinction between continuous-time and discrete-time signals, distinct signaling illustration exploitation advanced exponential and curving elements, regularity of distinct time exploitation advanced exponential signal, idea of Z- remodel of a distinct sequence. Distinction between Marquis de Laplace, Fourier and Z transforms. Region of convergence in Z-Transform, constraints on mythical monster for varied categories of signals, Inverse Z-transform, properties of Z-transforms.
TEXT BOOKS:
- Signals, Systems & Communications – B.P. Lathi, Bachelor of Science Publications, 2003. 2. Signals and Systems – A.V. Oppenheim, A.S. Willsky and S.H. Nawab, PHI, 2nd Edn. 3. Signals & Systems- Narayan Iyer and K Satya Prasad, Cengage Pub.
REFERENCE BOOKS:
- Signals & Systems – Simon Haykin and Van Veen, Wiley, second Edition. 2. Principles of Linear Systems and Signals – BP club, Oxford University Press, 2015 3. Signals and Systems – K Raja Rajeswari, B VisweswaraRao, PHI, 2009 4. Fundamentals of Signals and Systems- Michel J. Robert, MGH International Edition, 2008. 5. Signals and Systems – T K Rawat , Oxford University press, 2011
OUTCOMES:
At the top of this course the scholar can in a position to:
• Characterize the signals and systems and principles of vector areas, idea of orthgonality.
• Analyze the continuous-time signals and continuous-time systems exploitation series, Fourier remodel and Marquis de Laplace remodel.
• Apply sampling theorem to convert continuous-time signals to discrete-time signal and reconstruct back.
• perceive the relationships among the assorted representations of LTI systems
• perceive the ideas of convolution, correlation, Energy and Power density spectrum and their relationships.
• Apply z-transform to research discrete-time signals and systems.

by Rishi | Jul 17, 2019 | Jntuk lecture notes
POWER Electronics
Preamble:
The usage of power elctronics in day to day life has enhanced in recent years. it’s necessary for student to know the basic principles behind of these converters. This course covers characteristics of semiconductor devices, ac/dc, dc/dc, ac/ac and dc/ac converters. The importance of victimization pulse breadth modulated techniques to get prime quality power provide (dc/ac converter) is additionally mentioned very well during this course.
Learning Objectives:
• to check the characteristics of assorted power semiconductor devices and to style firing circuits for SCR.
• to know the operation of single part full–wave converters and analyze harmonics within the input current.
• to check the operation of 3 part full–wave converters.
• to know the operation of various styles of DC-DC converters.
• to know the operation of inverters and application of PWM techniques for voltage management and harmonic mitigation.
• to investigate the operation of AC-AC regulators.
UNIT–I:
Power Semi-Conductor Devices Thyristors–Silicon controlled rectifiers (SCR’s) –Characteristics of power MOSFET and power IGBT– Basic theory of operation of SCR–Static characteristics– activate and switch off methods–Dynamic characteristics of SCR– Snubber circuit design– Basic necessities of gating circuits for SCR, IGBT and MOSFET.
UNIT–II:
AC-DCSingle-Phase Converters 1-phase [*fr1] wave controlled rectifiers – R load and RL load with and while not freewheeling diode – 1-phase full wave controlled rectifiers – center tapped configuration and bridge configuration- R load and RL load with and while not freewheeling diode – continuous and discontinuous conductivity – result of supply inductance in 1-phase totally controlled bridge rectifier with continuous conductivity.
UNIT–III:
AC-DC3-Phase Converters 3-phase [fr1] wave and Full wave uncontrolled rectifier – 3-phase [fr1] wave controlled rectifier with R and RL load – 3-phase totally controlled rectifier with R and RL load – 3-phase semi controlled rectifier with R and RL load.
UNIT–IV:
DC–DC Converters Analysis of Buck, boost and buck, buck-boost converters in ContinuousConduction Mode (CCM) and Discontinuous conductivity Modes (DCM) – Output voltage equations victimization voltsec balance in CCM & DCM output voltage ripple current, ripple for CCM solely – Principle operation of forward and fly back converters in CCM.
UNIT – V:
DC–AC Converters 1- part halfbridge and full bridge inverters with R and RL masses – 3-phase sq. wave inverters – 1200 conductivity and 1800 conductivity modes of operation – PWM inverters – Quasi-square wave pulse breadth modulation – curved pulse breadth modulation – interference of shoot through fault in Voltage supply electrical converter (VSI) – Current supply electrical converter (CSI) – Introduction to motor vehicle ordered Commutated Current supply electrical converter (ASCCSI) .
UNIT – VI:
AC – AC Regulators. Static V-I characteristics of TRIAC and modes of operation – 1-phase AC-AC regulator point management and integrated cycle management with R and RL load – For continuous and discontinuous conduction- 3-Phase AC-AC regulators with R load solely – electrical device faucet ever-changing victimization parallel Thyristors.
Learning Outcomes:
Student ought to be ready to
• justify the characteristics of assorted power semiconductor devices and analyze the static and dynamic characteristics of SCR’s.
• style firing circuits for SCR.
• Explain the operation of single part full–wave converters and analyze harmonics within the input current.
• justify the operation of 3 part full–wave converters.
• Analyze the operation of various styles of DC-DC converters.
• justify the operation of inverters and application of PWM techniques for voltage management and harmonic mitigation.
• Analyze the operation of AC-AC regulators.
Text Books:
one. Power Electronics: Circuits, Devices and Applications – by M. H. Rashid, learner Hall of Bharat, 2d edition, 1998
2. Power Electronics: necessities & Applications by L.Umanand, Wiley, Pvt. Limited, India, 2009
Reference Books:
one. components of Power Electronics–Philip T.Krein.oxford.
2. Power natural philosophy – by P.S.Bhimbra, Khanna Publishers.
3. Thyristorised Power Controllers – by G. K. Dubey, S. R. Doradla, A. Joshi and R. M. K.Sinha, New Age International (P) restricted Publishers, 1996.
4. Power natural philosophy reference work by Muhammad H.Rashid, Elsevier.
5. Power Electronics: converters, applications -by Nedmohan, Tore M. Undeland, Jerome Robbins by Wiley Bharat Pvt. Ltd.
6. Power convertor Circuits -by William Shepherd, Li zhang, CRC Taylor & Francis cluster.

by Rishi | Jul 14, 2019 | Jntuk lecture notes
PULSE AND DIGITAL CIRCUITS OBJECTIVES
The student are going to be created
• to know the construct of wave shaping circuits, shift Characteristics of diode and electronic transistor.
• to review the look and analysis of assorted Multivibrators.
• to know the functioning of various forms of time-base Generators.
• to be told the operating of logic families & Sampling Gates.
UNIT I LINEAR WAVESHAPING:
High pass, low pass RC circuits, their response for curving, step, pulse, square, ramp and exponential inputs. RC network as mortal and integrator; Attenuators , its applications in electronic equipment probe, RL and RLC circuits and their response for step input, Ringing circuit.
UNIT II NON-LINEAR WAVE SHAPING :
Diode clippers, electronic transistor clippers, clipping at 2 freelance levels, Transfer characteristics of clippers, electrode coupled clipper; Clamping operation, clamping circuits mistreatment diode with completely different inputs, Clamping circuit theorem, sensible clamping circuits, impact of diode characteristics on clamping voltage, Transfer characteristics of clampers. [ads]
UNIT III shift CHARACTERISTICS OF DEVICES :
Diode as a switch, piecewise linear diode characteristics, style and analysis of electronic transistor as a switch, Break down voltage thought of electronic transistor, saturation parameters of electronic transistor and their variation with temperature, style of electronic transistor switch, transistor-switching times. Bistable Multivibrator: Analysis and style of fastened Bias, Self Bias Bistable Multi Vibrator, Collector Catching Diodes, Commutating Capacitors, Triggering of Binary Circuits, electrode Coupled Bistable Multivibrator (Schmitt Trigger).
UNIT IV Monostable Multivibrator:
Analysis and style of Collector Coupled Monostable Multi vibrator, Triggering of Monostable Multivibrator, Applications of Monostable Multivibrator. Astable Multivibrator: Analysis and style of Collector Coupled Astable Multivibrator, Application of Astable Multivibrator as a Voltage to Frequency device.
UNIT V VOLTAGE TIME BASE GENERATORS:
General options of a time base signal, ways of generating time base wave Exponential Sweep Circuits, Negative Resistance Switches, basic principles in Miller and Bootstrap time base generators, electronic transistor Miller time base generator, electronic transistor Bootstrap time base generator.
UNIT VI LOGIC FAMILIES & SAMPLING GATES:
LOGIC FAMILIES: Diode Logic, electronic transistor Logic, Diode-Transistor Logic, TransistorTransistor Logic, electrode Coupled Logic, AOI Logic, Comparison of Logic Families. SAMPLING GATES: Basic operational Principles of Sampling Gates, Diode unidirectional Sampling Gate and Two-Diode Bi-Directional Sampling Gate, Four-Diode gates, Six-Diode Gates, Reduction of Pedestal in Sampling Gates, Applications of Sampling Gates.
TEXT BOOKS:
1. Pulse, Digital and shift Waveforms – J. Millman and H. Taub, McGraw-Hill 2. Pulse and Digital Circuits – A. Anand Kumar, PHI, 2005
REFERENCES :
1.Pulse, Digital and shift Waveforms – J. Millman and H. Taub, Mothiki S Prakash Rao McGraw-Hill, Second Edition, 2007.
2. Solid State Pulse circuits – David A. Bell, PHI, 4th Edn., 2002
3. Pulse & Digital Circuits by Venkata Rao,K,Ramasudha K, Manmadha Rao,G., Pearson,2010
OUTCOMES [ads]
once researching this course the scholar are going to be able to
• style linear and non-linear wave shaping circuits.
• Apply the basic ideas of wave shaping for numerous shift and signal generating circuits.
• style completely different multivibrators and time base generators.
• Utilize the non curving signals in several experimental analysis areas.




